Note: Students taking this course should have completed either the Fundamentals of Electromagnetic Compatibility course, the Electronic Systems Design for EMC Compliance course, or the Design for Automotive EMC Compliance course.
Advanced Design for EMC Compliance
Description
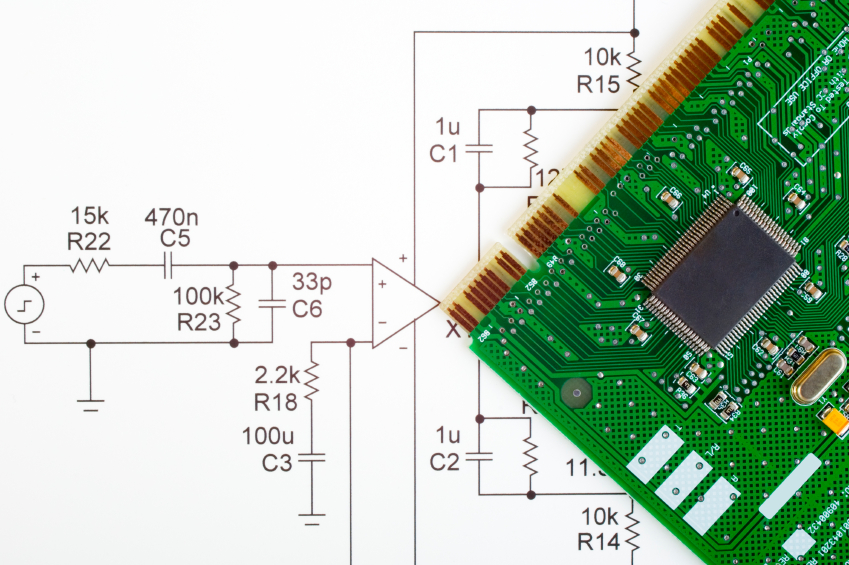
Electronic products should be designed to meet all electromagnetic compatibility requirements, then tested once to validate the design. A product that fails to meet EMC requirements the first time, and is subsequently redesigned and retested until it passes, will generally be more costly and less reliable than products designed to comply. Designing for EMC compliance is a systematic and cost-effective way to ensure that products won't have problems in the field, as compared to testing and fixing product designs after the first prototype is available.
Designing for EMC compliance is not a matter of following a set of design rules or sealing everything inside a metal enclosure. It is a systematic process of identifying and evaluating all EMC sources, victims and coupling paths within a system, as well as coupling between the system and its environment. Designing for compliance helps to ensure that products meet their cost and development schedule targets.
This 12-hour course leads students through the process of systematically ensuring that their product designs will meet all applicable EMC requirements. Students will learn to identify and utilize the ground structure, control the flow of high- and low-frequency currents, identify and characterize potential sources and victims of EMI, control bandwidths, ignore structures and coupling paths that do not contribute to EMC problems, and systematically identify and evaluate structures and coupling paths capable of causing a product to be non-compliant.
Continuing Education Credit: 1.2 CEUs, 12 PDHs
Course Outline


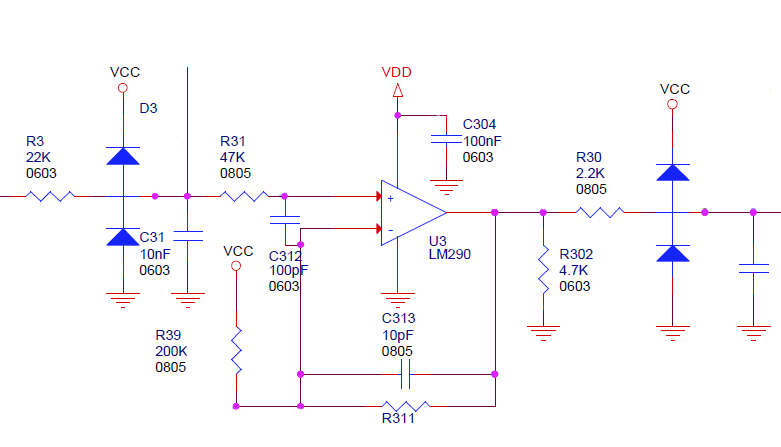
Part 1 - The Design for Compliance Approach
- Overview of Design for Compliance (DFC) Process
- Translating EMC test requirements to system design requirements
- Recognizing what's important
- Determining what you need to know (and what you can never know)
- Working with board layouts, schematics and system design/test specifications
- Maximum coupling calculations
- Defining the System
- Identifying the ground structure
- Identifying antennas/ports
- Identifying sources
- Identifying victims
- Coupling Mechanisms
- Important examples of common impedance coupling
- Important examples of electric field coupling
- Important examples of magnetic field coupling
- Effectively dealing with radiated coupling
- Narrowing the Focus
- Risetime/bandwidth control
- Eliminating unnecessary antennas/ports
- Eliminating unnecessary sources/victims
- Eliminating unnecessary requirements
- Effective utilization of return planes
- Dealing with What's Left
- Maximum emissions calculations
- Maximum crosstalk calculations
- Worst-case modeling
- The EMC design review
Part 2 - Ensuring Compliance with Each Requirement
- Ensuring Compliance with Conducted Emissions Requirements
- Identifying the sources
- Quantifying the coupling
- Avoiding common design pitfalls
- Example of the process applied to an actual product design
- Ensuring Compliance with Radiated Emissions Requirements
- Identifying the sources
- Quantifying the coupling
- Avoiding common design pitfalls
- Example of the process applied to an actual product design
- Ensuring Compliance with Radiated Immunity Requirements
- Identifying the sources and victims
- Quantifying the coupling
- Avoiding common design pitfalls
- Example of the process applied to an actual product design
- Ensuring Compliance with Bulk Current Injection Requirements
- Identifying the sources
- Quantifying the coupling
- Avoiding common design pitfalls
- Example of the process applied to an actual product design
- Ensuring Compliance with Electrical Fast Transient Requirements
- Identifying the sources and victims
- Quantifying the coupling
- Avoiding common design pitfalls
- Example of the process applied to an actual product design
- Ensuring Compliance with Electrostatic Discharge Requirements
- Identifying the sources and victims
- Quantifying the coupling
- Avoiding common design pitfalls
- Example of the process applied to an actual product design
- Utilizing Available Resources
- Utilizing experience with past products
- Utilizing modeling tools effectively
- Utilizing consultants effectively
- Information and tools available online
Course Instructor

Dr. Todd H. Hubing is a Professor Emeritus of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Clemson University and former Director of the Clemson Vehicular Electronics Laboratory. He and his students at Clemson have worked on the development and analysis of a wide variety of electronic products. EMC design rules can vary greatly depending on whether you are designing high-speed computing equipment, low-cost mixed-signal consumer products or high-power industrial controls; but the basic EMC principles are the same in all industries. By applying these principles in an organized manner, it is possible to review a design circuit-by-circuit to guarantee that any particular EMC requirement will be met. This approach is more effective than the blind application of design guidelines and is the primary emphasis of every EMC design class taught by Dr. Hubing.
